Correlation is the relationship between the price movements of two or more assets.
Positive correlation — assets rise or fall together.
Negative correlation — one asset rises while the other falls.
Understanding correlations helps traders anticipate movements in one market by observing changes in another.
Why Do Markets Correlate?
The main reason is the flow of capital between markets:
Rising demand for one asset → its price increases along with the related currency.
Falling demand → capital moves to other markets → opposite movement occurs.
Sometimes correlations break (e.g., during crises), when investors simultaneously seek safe-haven assets (like gold or US Treasuries), causing several assets to rise at once.
—
Key Correlation Examples
1. AUD and Gold (Positive)
Australia is a major gold exporter.
Rising gold prices → more currency operations in AUD → Australian dollar strengthens.
Trading idea:
If gold rises, look for opportunities to buy AUD/USD*
2. USD and Gold (Negative)
In “calm times”: investors prefer risk assets (US stocks) → sell gold → USD rises, gold falls.
In crises: capital moves to safe-haven assets (gold) → USD may weaken while gold rises.
In extreme market stress, both can rise (e.g., 2008 crisis).
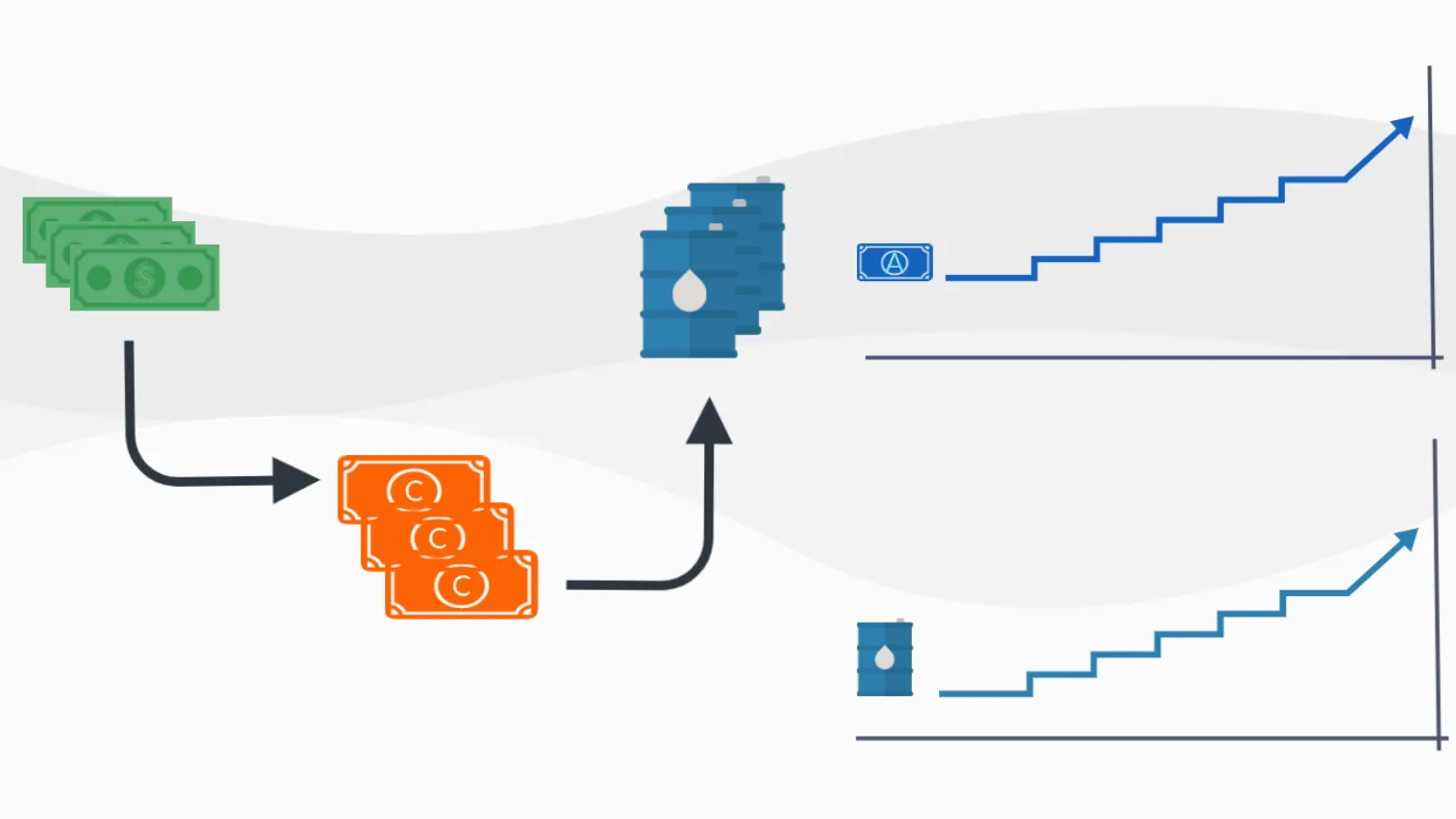
3. CAD and Oil (Positive)
Canada is one of the largest oil exporters (75% exported to the US).
Rising oil prices → increased demand for CAD → Canadian dollar strengthens.
Trading idea:
If oil prices jump (e.g., due to supply disruptions), consider buying CAD against USD.
4. CHF and Stock Markets (Negative)
The Swiss franc (CHF) is a safe-haven currency.
Falling stock indexes → investors flee to safety → CHF strengthens.
Trading idea:
On negative US economic data, look for buying opportunities in CHF against USD or EUR.
How to Use Correlation in Trading?
Signal confirmation — check related assets before entering a trade.
Hedging — reduce risks by opening opposite positions in negatively correlated assets.
Lead trading — movements in one market can help predict changes in another.
Conclusion:
Monitoring correlated markets provides valuable context for trading decisions, allowing traders to confirm signals, hedge risks, and anticipate price movements.

